Then the flap is tunneled laterally along the left or right colic gutter to the pelvic floor where it is attached to the peritoneal covering of the pelvis or wrapped around the coloanal anastomoses.
Pelvic colic gutter.
Mesenteric lymphadenitis is an inflammation of lymph nodes.
Etiologically it means a channel adjacent to the abdominal wall.
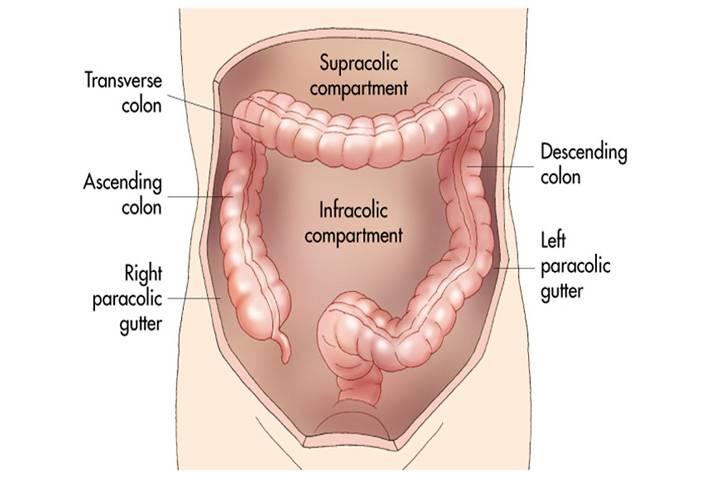
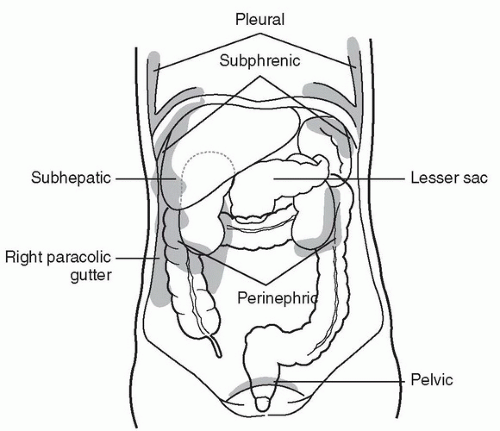
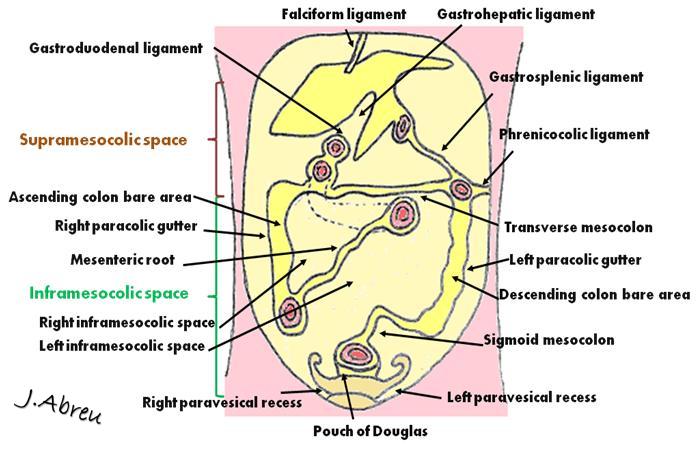
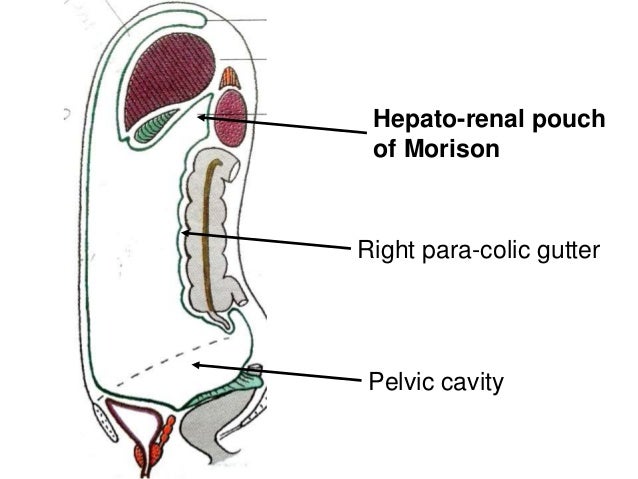
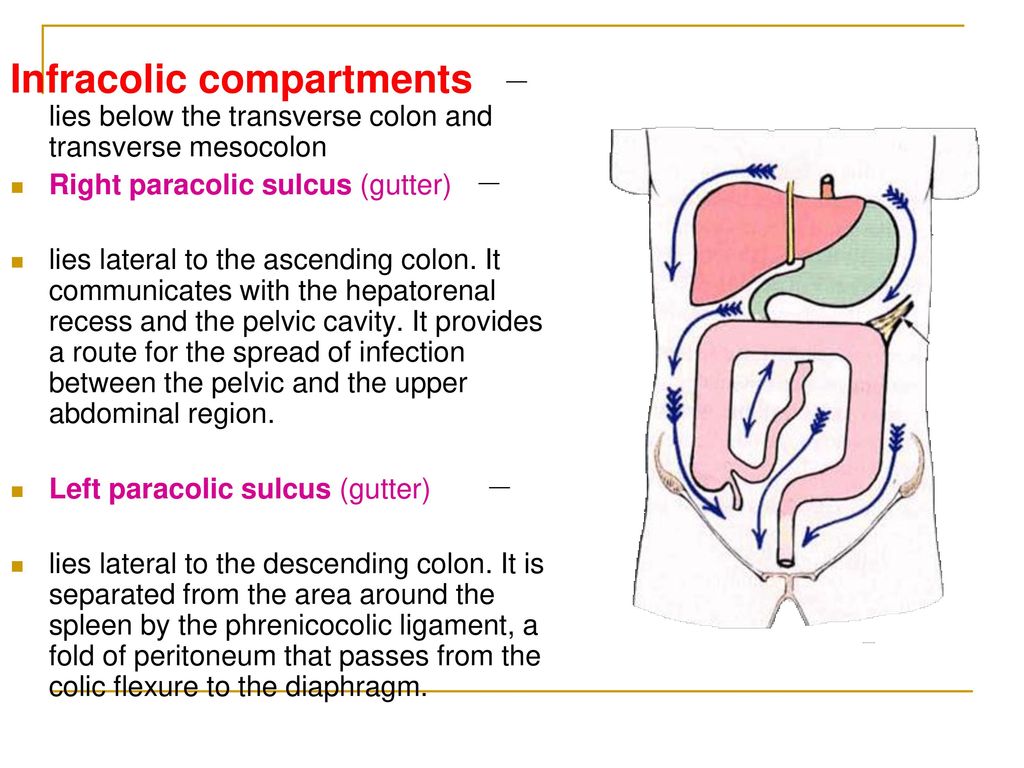
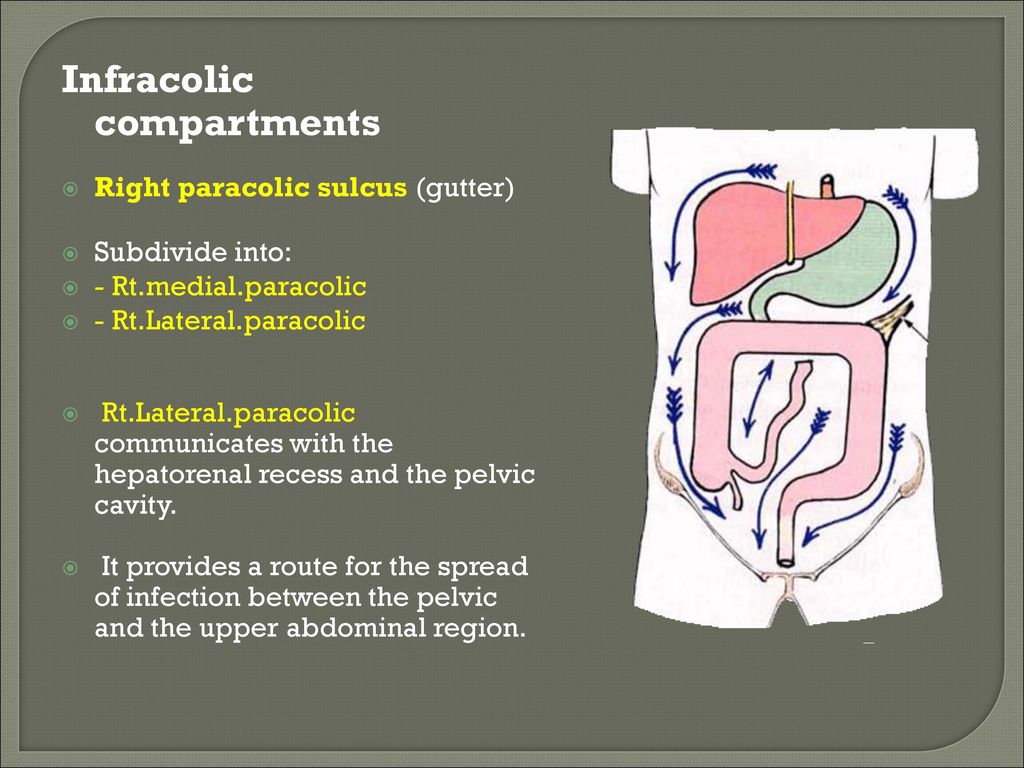
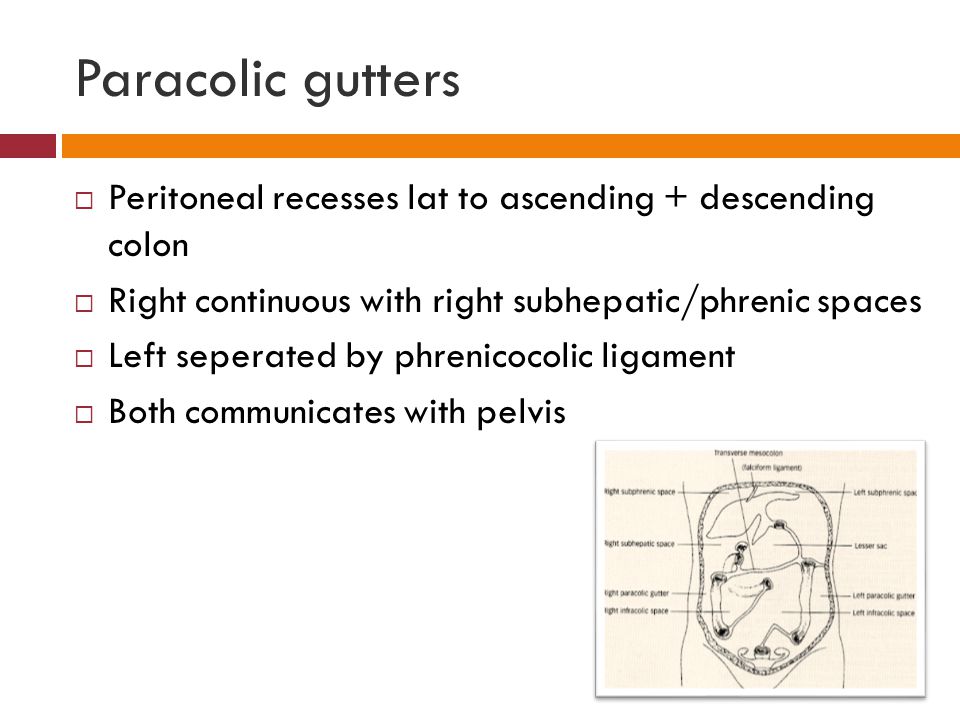
The right paracolic gutter is larger than the left and communicates freely with the right subphrenic space.
It extends from the right colic hepatic flexure surrounds the cecum and enters the pelvic cavity.
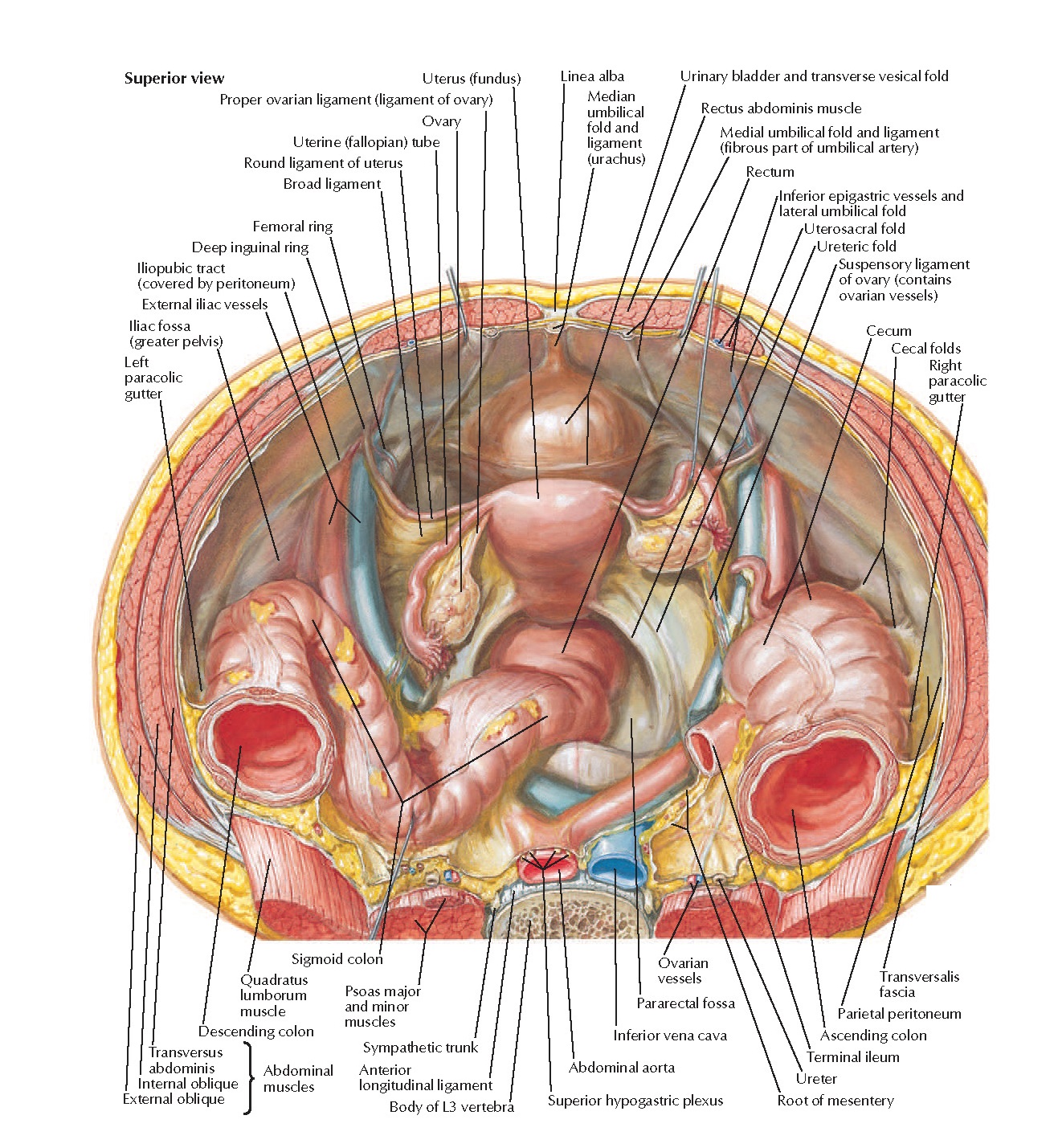
On the right hand side the right lateral paracolic gutter is found lateral to the ascending colon and medial to the lateral part of the anterior abdominal wall.
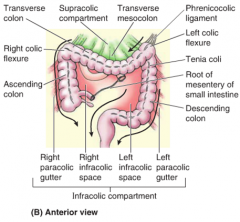
The left gutter runs between the descending colon and the abdominal wall and just like the right gutter empties into the lower abdomen and pelvic area.
It is also known as sulci paracolic and paracolic recesses.
Contraindications for the use of omental flaps include adhesions.
This gutter is however much smaller because it is restricted at the top by the phrenicocolic ligament or the ligament supporting the top left edge of the colon.
The right lateral paracolic gutter runs from the superiolateral aspect of the hepatic flexure of the colon down the lateral aspect of the ascending colon and around the cecum.
It is continuous with the peritoneum as it descends into the pelvis over the pelvic brim.
Chronic pelvic pain can result from more than one condition.
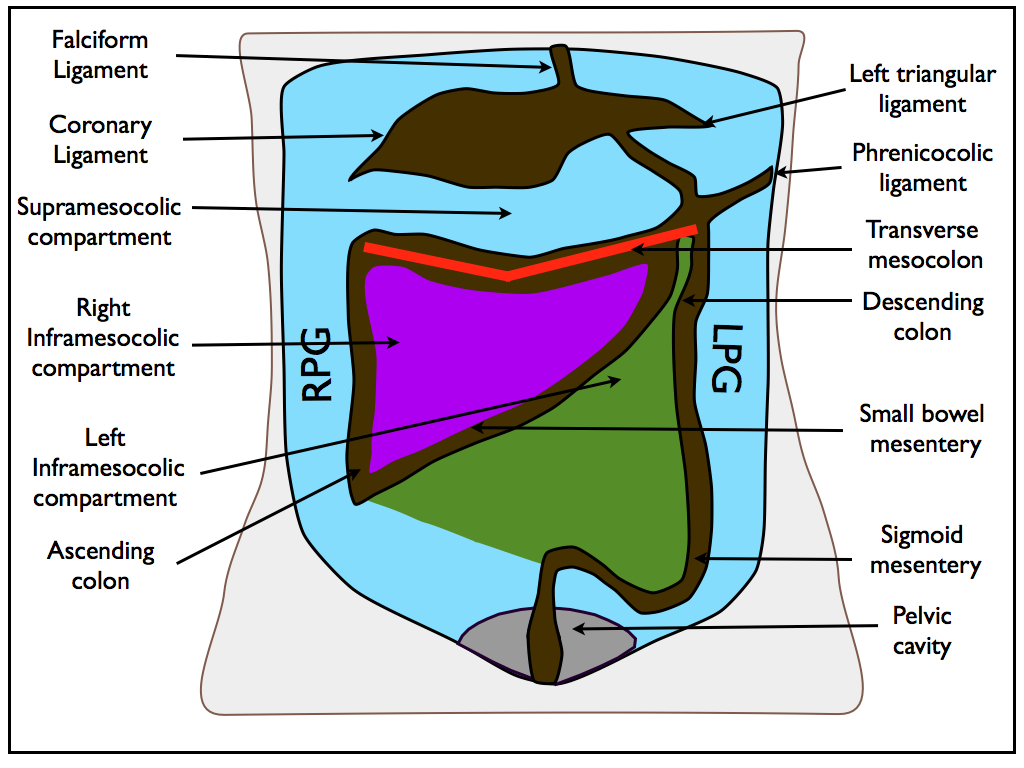
The paracolic spaces gutters are located lateral to the peritoneal reflections of the left and right sides of the colon fig 8a.
Between the outer wall of the colon and back side of the abdominal wall there is an open space known as the paracolic gutter.
The lymph nodes that become inflamed are in a membrane that attaches the intestine to the abdominal wall.
Right colic flexure anterior view right medial paracolic gutter.
It is the depression between the postero lateral wall of the abdomen and the lateral margins of the ascending and descending colon.
These lymph nodes are among.
Recently doctors have recognized that some pelvic pain particularly chronic pelvic pain can also arise from muscles and connective tissue ligaments in the structures of the pelvic floor.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/1272/Supracolic_compartment.png)