Radiological considerations in the setting of orbital roof fracture it is important to fully assess the extent of the fracture including any radiographically apparent concomitant abnormalities.
Orbital roof fracture radiology.
Although common in the pediatric population isolated orbital roof fractures can also occasionally occur in an adult fig 13.
The injury can be associated with a violation of the dura necessitating an intracranial approach.
Most roof fractures are associated with other orbital fractures and result from significant head trauma as a high degree of force is required to fracture this portion of the orbit.
The orbital roof is composed of the orbital plate of the frontal bone with a small contribution from the lesser wing of the sphenoid at the apex figures 3 4 and 3 5.
Fracture of the left zygomaticomaxillary attachmnet with fracture of the anterior and lateral maxillary walls inferior orbital rim fracture and left maxillary hemosinus.
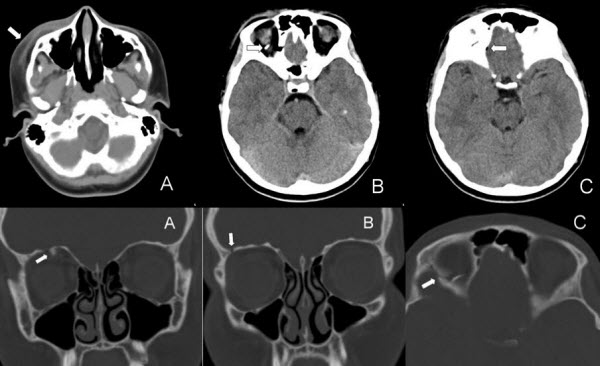
Displaced orbital roof fracture 3.
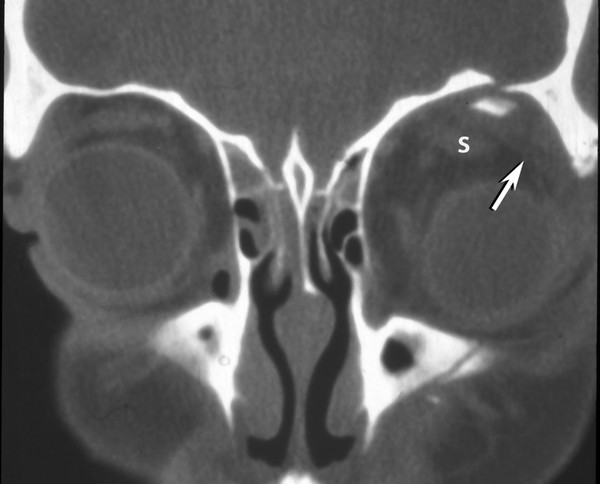
Orbital blowout fractures occur when there is a fracture of one of the walls of orbit but the orbital rim remains intact.
A orbital fractures can occur in isolation or with other fracture patterns.
Assessing traumatic orbital injuries is an important challenge for radiologists.
Very rarely the orbital roof will fracture without displacement of fractures fragments resulting in the non displaced orbital roof fracture.
This is typically caused by a direct blow to the central orbit from a fist or ball.
A three dimensional ct reconstruction demonstrated the extent and shape of the skull fracture fig.
Orbital roof fracture icd 801 01 etiology.
Radiological considerations in the setting of orbital roof fracture it is important to fully assess the extent of the fracture including any radiographically apparent concomitant abnormalities.
Orbital fracture pearls are as follows.
This assessment is even more difficult when the orbital injury is associated with injuries involving multiple organs.
It is a thin lamina separating the orbit anteriorly from the frontal sinus and posteriorly from the anterior cranial fossa.
Isolated orbital roof fractures in adults are uncommon comprising 12 19 of all orbital wall fractures.
Dr robert foley and assoc prof frank gaillard et al.
Communited mildly depressed left orbital roof fracture.
Angulated displaced fractures fragments are seen projecting downwards within the orbit indenting the superior rectus muscle.
Fractures of the orbital roof are usually seen in combination with extension of linear frontal bone fractures or with complex cranial facial fractures including le fort iii naso orbito ethmoidal noe skull base fractures extending into the anterior skull base.